How does trade unions affect labour wages
Trade Unions can play a vital role in affecting the wage rate in the industry.
Their methods have the result of either increasing the demand for labor or by either restricting the supply of substitutable labor, such as by restricting immigration, or by promoting benefits that have, as a side benefit, the effect of restricting labor supply, such as restricting the number of hours that each worker can work or by allowing early retirement.
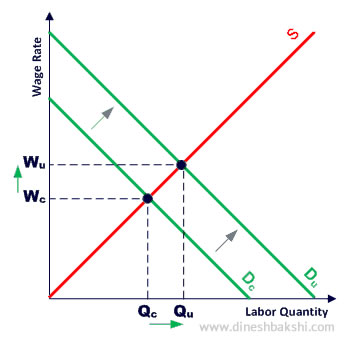
By increasing the demand for labour
Sometimes unions help the employer to advertise the products that the business produces, or they may advertise to persuade consumers to buy union products. Unions also lobby politicians to increase spending on services provided by union members, such as when teachers' unions lobby for increased spending on education. Labour demand increases as the demand for those products increase.
The diagram below illustrates the effect. As the demand for labour increase (Dc to Du), the wage rates increase from Wc to Wu.
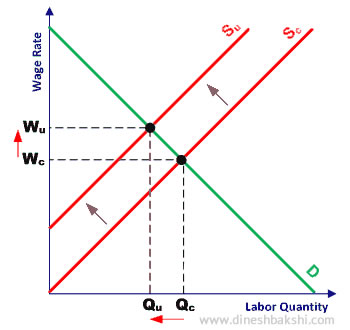
By restricting the supply of labour
Craft unions organize their members by trade, such as printers or shoemakers. They restrict their membership by requiring long apprenticeships and charging high initiation fees. Moreover, many craft unions have successfully compelled firms to hire only unionized labor, so by restricting the supply of their own membership, they increase the wages that they can earn. Craft unions' means of raising wages by restricting membership is often referred to as exclusive unionism.
Many professional organizations use occupational licensing as a means to limit membership, such as laws requiring a medical license to practice medicine or a law license to practice law. Plumbers, electricians, and carpenters, and other members of the construction trade most often require licenses to work in their trade. Even occupations that do not require a lot of skill, such as cosmetology or cutting hair, often requires practitioners to have licenses, and licensing requirements are frequently more onerous than necessary to perform a job well. A primary objective of licensing is to reduce membership, thereby increasing the competition for labor.
As the diagram illustrates, a fall in supply of labour (shift of supply curve to the left) leads to wages increase from Wc to Wu