Fiscal Policy -The government budget
According to Encyclopaedia Britannica
government budget, forecast by a government of its expenditures and revenues for a specific period of time.
In national finance, the period covered by a budget is usually a year, known as a financial or fiscal year, which may or may not correspond with the calendar year.
As mentioned above, the government budget has two aspects, the revenue and the expenditure.
Watch a video on Budget
Let’s discuss these aspects in detail.
Government Revenue
The main sources of government revenue are:
Taxes: These taxes comprise of both direct and indirect taxes. Taxes for a major source of government revenue. The chart below shows a source of government revenue for UK. Most of the nations have similar pattern of revenue sources.
Sale of goods and services: Many governments owned business earn substantial amount of revenue for the government. This can be another major source of revenue for the government.
Sale of state owned enterprises: Government might also earn revenue by selling state owned businesses to private sector. This is particularly seen in countries where a lot of privatisation is taking place. This is not a regular source of government’s revenue and differs substantially among countries.
Government Expenditure
Government expenditure is the total amount spent by the government in the economy. It can be classified as

Capital expenditure is the government spending on acquisition of goods and services intended to create future benefits, such as infrastructure investment or research spending.
Current expenditure is the expenditure of the government which does not result in the creation of assets or reduction in the value of its liabilities. Such expenditures are incurred for the normal running of government departments and maintenance of services.
Transfer payments is the financial assistance given to sections of the society in order to uplift or maintain their standard of living.Governments use such payments as means of income redistribution by giving out money under social welfare programs such as social security, old age or disability pensions, student grants, unemployment compensation, etc.
Given below is government expenditure for UK. Most of the countries have similar pattern of government expenditure. However, there might be different patterns based on priorities and policies and the political ideology of the government.
Budget outcomes
Budgets can have deficits or surplus. In a budget having more government spending than its revenue is termed as a deficit budget. Whereas, a budget with more government revenue than its expenditure is termed as a surplus budget.
Government budget deficits can be cured by cutting spending, raising taxes or a combination of the two. Deficits must be financed by borrowing money. Interest must be paid on borrowed funds, which worsens the deficit.
Watch a Video
USEFUL LINKS
Sources of revenue US fedral Government
A SURVEY OF UK TAX SYSTEM (PDF)
The role of fiscal policy
Fiscal policy refers to government policy that attempts to influence the direction of the economy through changes in government taxes or through some spending.
The two main instruments of fiscal policy are government spending and taxation.
Changes in the level and composition of taxation and government spending can impact on the following variables in the economy:
- Aggregate demand and the level of economic activity.
- The pattern of resource allocation.
- The distribution of income.
AD=C+G+I+(X-M)
As we can see in the above equation that G (Government Expenditure) is a component of AD, it can be used by Government to influence AD in the economy. The government can use expansionary or deflationary fiscal policy to get the desired results. Let’s discuss each policy in detail.
Expansionary fiscal policy
Expansionary fiscal policy is used to increase the Aggregate demand in the economy. If the economy is having a deflationary gap, the government can use expansionary fiscal policy to reduce the gap or totally eliminate it.
Now, what is deflationary gap?
Deflationary gap is the difference between full level of employment and the actual level of output of the economy. We can see in the diagram below, that the economy is operating a level ‘a’ below the Yf (full level of employment).
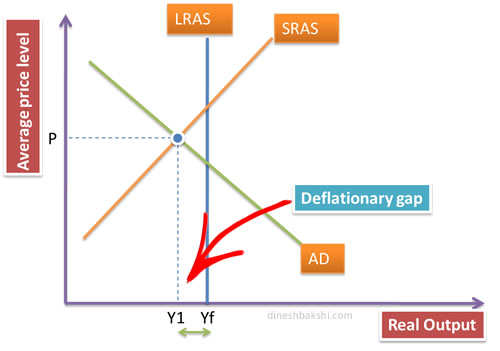
The consequence is that due to deflationary gap all the resources of the economy are not being used in the optimum level and they are idle. This results in unemployment and low level of output. This is not desirable for any government. In order to reduce/eliminate the deflationary gap, the government uses expansionary fiscal policy.
Government will either increase its spending or reduce taxes (or both) in order to stimulate the aggregate demand. Increase Government spending will result me more projects being funded by the government and thus employment and output will increase. Even a lower tax rate will result in more disposable income for households and encourage consumption.
Increased G and C will lead to higher AD. However, this might also lead to higher prices/inflation in the economy.
Contractionary fiscal policy
Contractionary fiscal policy involves the reduction of government spending and increase taxes as a measure to control inflation/AD in the economy. With reduced government spending, the AD will fall and thus reduce pressure on the economic resources and the average price level in the economy will come down. Similarly, increased taxes will take away the excess disposable income from the households and result in a fall in AD. Contractionary fiscal policy is thus used to reduce the inflationary gap.
But, what is inflationary gap?
Inflationary gap is when the Aggregate demand exceeds the productive potential of the economy. As we can see through the diagram, the economy is operating at a level above the full employment level of the output. Due the limitation of the economy to fulfil this increased demand the average price level in the economy increases resulting in inflation.
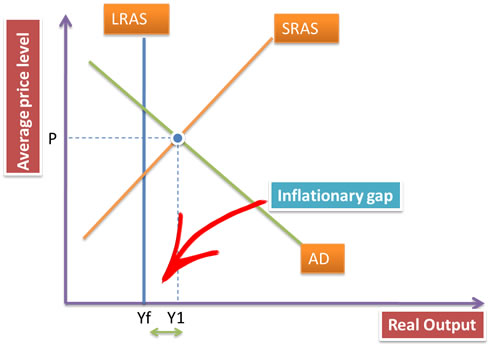
In this case the government can use contractionary fiscal policy to control inflation and bring down the AD.
Watch a Video
Fiscal policy is a powerful tool in the hands of the government. Fiscal policy can promote long term economic growth by increased government spending different sectors of the economy. With a careful planning of expenditure on capital goods in the economy i.e. infrastructure, better education and health systems, government can considerably improve the potential output in the economy. Better education and health will also result in improved human capital. Thus, improving the very basic factors of production available in the economy.
Moreover, a skilled labour force supported by a strong infrastructure will create a positive environment for firms to invest. The economy will find it easy to attract foreign capital. All these factors will lead to an increased economic growth.
Evaluating Fiscal Policy
Role of Taxation in promoting equity
What is a tax?
Tax is a fee charged ("levied") by a government on a product, income, or activity.
Why taxes are imposed?
There are different reasons for imposing taxes.
- To finance government expenditure. One of the most important uses of taxes is to finance public goods and services, such as street lighting and street cleaning.
- To reduce consumption of goods that creates negative externalities.
- To control the amount of imported goods i.e. tariffs
- Used as a part of fiscal policy to control aggregate demand in the economy.
- To control income inequality.
Types of taxes
Direct Taxes
It is a tax paid directly to the government by the persons on whom it is imposed.
Examples
- Tax imposed on peoples’ income-Income tax
- Tax on wealth – wealth Tax
- Tax on firm’s profits.- corporate tax
Further reading CLICK HERE
Indirect Taxes
Indirect tax is a tax collected by an intermediary (such as a retail store) from the person who bears the ultimate economic burden of the tax (such as the consumer). The intermediary later files a tax return and forwards the tax proceeds to government with the return.
Indirect taxes are generally included in the price of goods and services, so are less obvious to those paying the taxes than direct levies. Thus indirect taxes are also known as expenditure tax or consumption based tax.

Examples
- GST (Goods and service tax)
- VAT (Value added tax)
- Consumers are charged a percentage of tax while purchasing a good/service and then the seller pays the tax collected to the Government.
Download this document for further reading on Indirect tax http://download.nos.org/srsec311new/L.No.40-A.pdf
Other measures to promote equity
The governments also undertake expenditures to promote income equity. These include
Subsidies
Provide directly, or to subsidize, a variety of socially desirable goods and services. These include health care services, education, and infrastructure that include sanitation and clean water supplies.
Transfer payments
Government provide various kind of assistance to low income groups in the society. The objective is to support them in maintaining a reasonable standard of living and to lower inequality. These payments are given directly to these groups in the form of monetary help. Examples include Social Security, unemployment compensation, welfare, and disability payments.



